Formulation Supplied at 0.5 mg/ml in Tris saline, 0.02% sodium azide, pH7.3 with 0.5% bovine serum albumin.
| |
Unit Size 100 µg | |
Storage Instructions Aliquot and store at -20°C. Minimize freezing and thawing. | |
Synonym / Alias Names prostatic acid phosphotase|PAP|ACP3|ACP-3|acid phosphatase, prostate|ACPP | |
Usage Summary Immunofluorescence:: This antibody has been successfully used in IF on Mouse: Nousiainen HO et al. (2014) PMID: 24846136. | |
Accession ID NP_001090.2 | |
Blocking Peptide EBP09390 | |
Immunogen Peptide with sequence C-YGIHKQKEKSRLQ, from the internal region of the protein sequence according to NP_001090.2. | |
Product Comments This antibody is expected to recognize both isoforms (NP_001090.2; NP_001127666.1). | |
Peptide Sequence C-YGIHKQKEKSRLQ | |
Purification Method Purified from goat serum by ammonium sulphate precipitation followed by antigen affinity chromatography using the immunizing peptide. | |
Shipping Instructions Refrigerated | |
Predicted Species Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Cow | |
Reactive Species Human, Mouse | |
Human Gene ID 55 | |
Mouse Gene ID 56318 | |
Rat Gene ID 56780 | |
Product Grade  | |
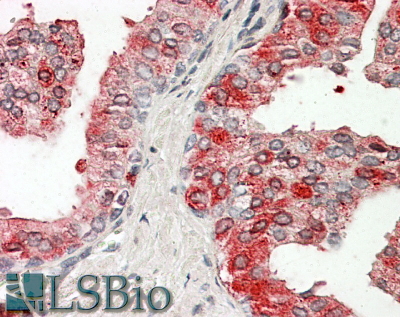
IHC Results In paraffin embedded Human Prostate shows cytoplasm staining in some secretory cells of the gland. Recommended concentration, 3-5µg/ml. This antibody has been successfully used in IHC on Mouse: Nousiainen HO et al. (2014) PMID: 24846136. | |
ELISA Detection Limit Antibody detection limit dilution 1:64000. | |
Western Blot Approx 50kDa band observed in Human Prostate lysates (calculated MW of 44.6kDa according to NP_001090.2). The observed molecular weight corresponds to earlier findings in literature with different antibodies (Patel et al, ,Clin Chem. 1986 Oct;32(10):1832-5. PMID: 3530530). Recommended concentration: 0.3-1µg/ml. | |
Application Type Pep-ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
Goat Anti-ACPP / PAP Antibody
$431.00
| SKU | Unit Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
Select a unit size:
Selected References [{"pmid": 24846136, "intro": "This antibody has been successfully used in IHC and IF on Mouse:", "title": "Mice deficient in transmembrane prostatic Acid phosphatase display increased GABAergic transmission and neurological\r\nalterations.", "author": "Nousiainen HO, Quintero IB, Myöhänen TT, Voikar V, Mijatovic J, Segerstråle M, Herrala AM, Kulesskaya N, Pulkka AE, Kivinummi T, Abo Ramadan U, Taira T, Piepponen TP, Rauvala H, Vihko P.", "journal": "PLoS One. 2014 May 20;9(5):e97851."}] |
Documents |